Research Blog & News
The launch of the Mac4Me project
Dresden, 19.02.2025

The European doctoral network Mac4Me (Macrophage Targets for Metastatic Treatment) launched with a virtual meeting on February 12th, 2025. Simultaneously, it also launched its digital and social media presence through its website and channels on LinkedIn and BlueSky.
Mac4Me is a 48-month project that addresses both technical and social challenges in cancer metastasis, focusing on three tumor types that show poor response to current immunotherapies: neuroblastoma, breast, and prostate cancer. These reflect the cancer development across a person’s lifetime and share metastatic disease spreading to the brain, bone, and liver.
Working alongside researchers and patients, the network will train 18 Doctoral Candidates to study the tumor microenvironment at metastatic sites, with a particular focus on the macrophage immune cell population. It will combine organ-on-chip technology with microfluidic systems to investigate early cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions during tumor invasion. Mac4Me will move beyond traditional “thinking in boxes” approaches by integrating bioinformatics and Artificial Intelligence solutions with real-world clinical data. The project will maintain a focus on patient experiences and translate scientific advances into meaningful outcomes.
Mac4Me is a Horizon Europe MSCA (Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions) Doctoral Network. The project is coordinated by Dr. Wytske van Weerden and Dr. Franziska Linke, Department of Urology at the Erasmus University Rotterdam. Prof. Dr. Martina Rauner, Scientific Director of the BoneLab Dresden at the Medical Clinic 3, is in charge of work packages 5 and 8, which are being carried out here at the Medical Faculty of TU Dresden with two international doctoral students. Further partners are the Delft University of Technology; the Erasmus University Rotterdam; GeneVia Technologies; the Oslo University Hospital; PeptimatrixTM; React4Life; the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland; the Science, Communication and Society Studies Centre at Universitat Pompeu Fabra; the University of Heidelberg; the University of Helsinki; the University of Nottingham; and the University of Bern. An additional 11 associated partners will contribute to the project. These entities represent an international network of universities, companies, patient associations, scientific associations, and a foundation from European countries (Finland, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Norway, The Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, and United Kingdom) and beyond (Australia, USA). The partnership brings together experts from multiple disciplines, including basic science, biomedical engineering, translational research, social sciences, and computational biology.
The aim of the EU network is to support the best minds in Europe in the various phases of their scientific careers, in addition to providing scientific knowledge. Mac4Me promotes the innovative and structured training of young scientists for up to four years on their way to an independent career.
For more information, visit the website.
For media inquiries, please contact: mac4me@upf.edu.

Neue Therapien für PatientInnen mit chronischem Parathormonmangel
Dresden, 16.08.2024
Ein chronischer Parathormonmangel (Hypoparathyreoidismus) ist in den meisten Fällen Folge einer Operation an der Schilddrüse, bei der die Nebenschilddrüsen entweder entfernt, oder irreversibel zerstört wurden.
Unbehandelt oder konventionell therapiert schädigt er langfristig das Nieren- und Gefäßsystem, kann zu Herzrhythmusstörungen und Krampfanfällen führen und auch neuropsychiatrische Symptome, wie Depression, Gedächtnis- und Angststörungen auslösen. Da Schilddrüsenerkrankungen häufiger bei Frauen, als bei Männern auftreten, werden etwa 76 % aller Fälle eines chronischen Hypoparathyreoidismus bei Frauen diagnostiziert.
Bis vor kurzem war die Therapie des Hypoparathyreoidismus eine der letzten endokrinen Erkrankungen, bei der nicht das fehlende Hormon ersetzt wurde, sondern durch Gabe von Vitamin D, Vitamin D-Analoga und Kalziumpräparaten versucht wurde, die Elektrolytstörungen (Kalziummangel und Phosphatüberschuss) auszugleichen. Die PatientInnen mussten eine Vielzahl an Tabletten einnehmen, die jedoch häufig schlecht vertragen wurden und früher oder später zu einem Absetzen der Therapie führten.
Einen vielversprechenden neuen Therapieansatz bietet das PTH-Analogon Palopegteriparatid, welches im Rahmen der PaTHway Phase-3-Studie auf seine Wirksamkeit, Sicherheit und Verträglichkeit untersucht wurde.
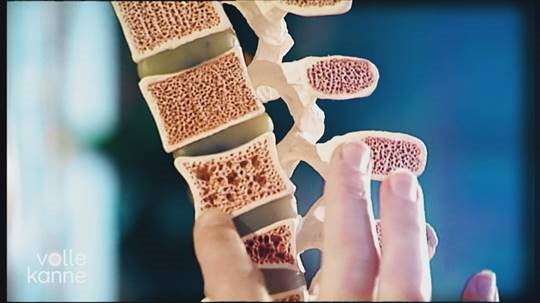
Volkskrankheit Osteoporose – so bleiben auch im Alter die Knochen stark
Dresden, 24.10.2023
Prof. Lorenz Hofbauer, Leiter des Bone Labs in Dresden, informierte am 20.10.2023, dem „Welt-Osteoporose-Tag“, über die Diagnose und Therapie der Osteoporose im ZDF-Magazin „Volle Kanne – Service täglich“. Neben den Risikofaktoren geht er auch auf die Entstehung und Behandlung ein. In vielen Fällen lässt sich durch Bewegung und Ernährung eine Verbesserung der Situation erreichen. Osteoporose sollte daher auch schon für jüngere Menschen ein Thema sein. Das ganze Interview und weitere Informationen hier: https://www.zdf.de/nachrichten/panorama/osteoporose-symptome-vorbeugung-100.html#xtor=CS5-95

Congratulations to Franziska Lademann, PhD – 2022 Recipient of the Friedrich Heuck Osteologie Award
Rewarding three of her original publications about the effects of thyroid hormones on bone, Franziska received this year’s Friedrich Heuck Osteologie Award sponsored by the Deutsche Akademie der osteologischen & rheumatologischen Wissenschaften e.V. (DAdorW).
Dresden, 21.12.2022
Thyroid hormones are essential regulators of skeletal growth and bone metabolism. In her first paper „Lack of the thyroid hormone transporter Mct8 in osteoblast and osteoclast progenitors increases trabecular bone in male mice“ Franziska investigated the role of the thyroid hormone transporter MCT8 in bone cells using different transgenic mouse models and showed that MCT8 directly affects bone remodeling and bone mass.
With the study “The thyroid hormone transporter MCT10 is a novel regulator of trabecular bone mass and bone turnover in male mice”, published 2022 in Endocrinology, another important thyroid hormone transporter in bone, MCT10, was identified and described to have distinct effects on bone structure and fragility in a site- and age-dependent manner.
Franziska’s third original publication, published 2021 in JBMR ,„Disruption of BMP signaling prevents hyperthyroidism-induced bone loss in male mice”, showed that the bone morphogentic protein (BMP) signaling pathway, one of the most important osteogenic signaling pathways, is activated by thyroid hormones in osteoblasts and its pharmacological blockade prevented the development of osteoporosis in hyperthyroid mice.
Franziska is now expanding her research and will focus on the interaction of thyroid hormone receptors and the BMP signaling pathway in bone.
We are proud of having such motivated and aspiring scientists in our Bone Lab. Keep up the good work, Franzi!

April 23 is International FOP Awareness Day 2022!!
Dresden, 23.04.2022
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP) is an ultra-rare severely disabling genetic disease affecting 1 in 1.5 million people. It is characterized by excessive heterotopic ossification that progressively limits movement. Patients suffer from malformed big toes and bone formation in muscles, tendons, ligaments and other connective tissues. FOP results from mutations in the ACVR1 gene, which encodes for the BMP type I receptor ALK2. These mutations lead to hyper-responsiveness of this receptor to various ligands of the TGFb/BMP superfamily.
Since the University of Pennsylvania announced their breakthrough discovery of the FOP gene ACVR1 at April 23, 2006, this date is now celebrated as International FOP Awareness Day! This year marks the 16th anniversary of the discovery of the FOP gene meaning 16 years of hope, progress and determination to find a cure.
Martina Rauner and Ulrike Baschant, two scientists from the Bone Lab Dresden, are trying to find new therapeutic approaches to abrogate heterotopic ossification. To support the FOP community, they are also wearing T-shirts to raise awareness for the 2022 Global FOP Awareness Day.
For more information and if you wish to support the FOP community, too, please visit: https://www.ifopa.org/2022_global_awareness_day
Hope. Believe. Wish. for a future without FOP.

Congratulations to Manuel Gado for defending his Ph.D. thesis with magna cum laude!
For his doctoral studies in the field of endocrinology, Manuel investigated the interaction between glucocorticoid signaling and the sympathetic nervous system in both the skeleton and the adipose tissue.
Dresden, 15.12.2021
To that end, he used two methods to activate the adaptive thermogenic capacity in mice: long-term cold acclimatization and a chronic administration of a β3-AR agonist. He demonstrated that activation of the beta-adrenergic system either with long-term cold acclimation or pharmacological β3-AR activation prevented the onset of glucocorticoid-induced adipose dysfunction and related metabolic comorbidities. Thus, targeting β3-AR may be regarded as a potential therapeutic strategy to prevent glucocorticoid-induced metabolic disease.
Manuel will continue working as a postdoc in Holger Henneicke’s lab focusing on the interaction between glucocorticoids and IL4 in skeletal biology at the CRTD in Dresden.
Keep up the good work, Manuel!

Congratulations to Giulia Furesi for defending her Ph.D. thesis with summa cum laude!
For her doctoral studies in the osteooncology field, Giulia focused on the role of extracellular vesicles in bone-prostate cancer cell crosstalk.
Dresden, 23.07.2021
Her research emphasizes the importance of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles in intercellular communication and underlines their impact on altering the physiological behavior of distant target cells, specifically osteoblasts. Moreover, Giulia’s results suggest that uptake of PCa-derived exosomal miRNAs by osteoblasts might contribute to the formation of metastatic bone lesions. This project would have not been possible without the successful collaboration within the µBONE consortium. As her next career step, Giulia will join the lab of Professor Roberta Faccio, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, USA, as a postdoc in September 2021. We are so proud of her and wish her all the best for her future scientific career!

Congratulations to Maria Ledesma Colunga and Giulia Furesi on their great achievements at the ECTS Digital Congress 2021!
Dresden, 17.05.2021
Giulia Furesi and Maria Ledesma Colunga, both young scientists from the Dresden Bone Lab, received the opportunity to present their research on the ECTS Digital Congress 2021 in form of an oral presentation.
Giulia Furesi presented her PhD thesis work in the osteooncology field as an oral presentation in the basic/translational session: Cancer, Regeneration and Stem Cells with the title: “Extracellular vesicles from metastatic prostate cancer modulate osteoblastic functions”. Her abstract has been selected for the ECTS Travel Award.
Maria Ledesma Colunga, a Postdoc interested in osteohematology and osteimmunology, presented her latest results in the session Progress in Translational Research as a plenary oral presentation, entitled “Deletion of Transferrin Receptor 2 (Tfr2) aggravates inflammation and bone erosion by promoting macrophage activation in inflammatory arthritis”. Moreover, Maria obtained the New Investigator Award for her Abstract.
We are proud of having such highly motivated and ambitious young scientists in our Bone Lab!

